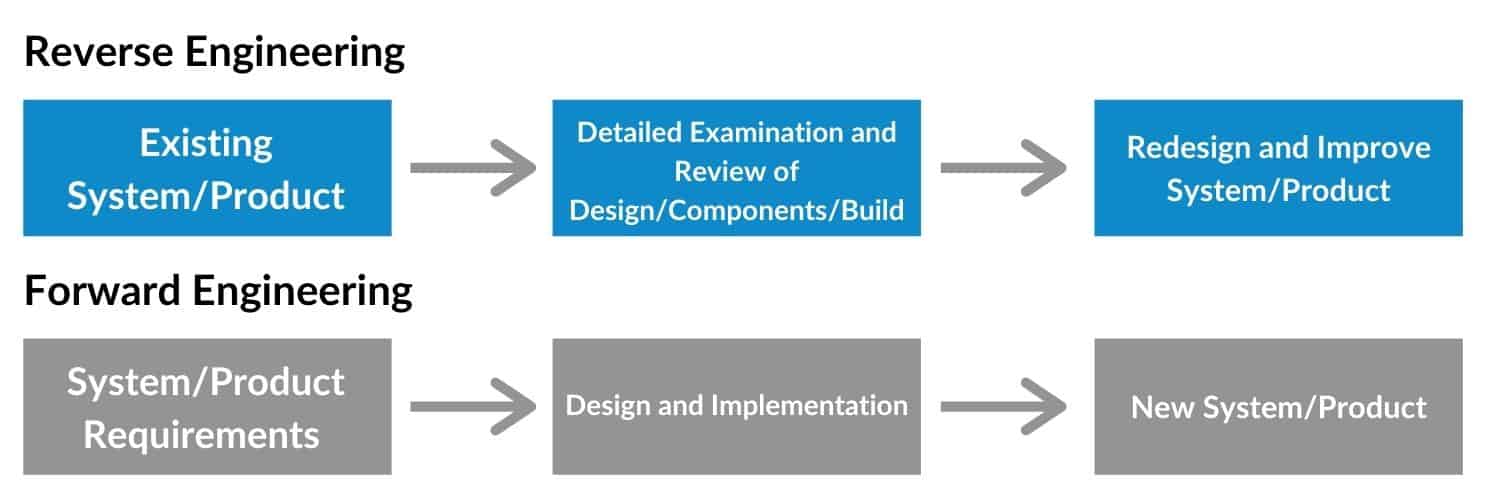
Although reverse engineering and forward engineering are closely related, there are some crucial differences. Let’s take a closer look.
What is Reverse Engineering?
Reverse engineering, also known as backward engineering, is the process of collecting information from a given or existing product (e.g., a software package, a network, or a system). It involves tearing down the product to extract knowledge of its internal components and reproducing its internal designs (e.g., architecture, circuitry, processes, code, structure, or material) following a detailed examination of its construction or composition. The reason to perform reverse engineering varies and it could be applied to anywhere from product development to cybersecurity to infringement litigation.
What is Forward Engineering?
Forward engineering is associated with conventional development of the same application. It is a method of creating or making a product from scratch with the help of the given system requirements. In this, the requirements are provided before the development of the application. Forward engineering process begins with system specification, followed by design and implementation, and culminates in a new system creation.
What is the Difference Between Forward and Reverse Engineering?
The crucial difference between the two is that forward engineering starts from a set of designs and develops the product based on those designs. On the other hand, reverse engineering starts from the product itself and attempts to derive the original designs that are embedded in the product. As such, a forward engineering, the goal is the development of a product (or a system, a protocol, a network, an integrated circuit, a software package, or whatever the end product is).
Applications of Reverse Engineering
Hardware reverse engineering and re-engineering are handy in designs if the original design architectures are unknown, lost, or only partially available. Equally, software reverse engineering for legacy software systems helps solve incorrect or incomplete documentation. Through tear-down analysis and reverse engineering, discovering an object’s original design or process is attempted to duplicate or enhance the design or process.
Reverse engineering may also be used in detection and proof of infringement on intellectual property rights.
Benefits of Reverse Engineering
- Provides insight into the original designs to reconstruct out-of-date or faulty products.
- Uncovers product vulnerabilities, which can protect users’ safety.
- Examining existing designs and maneuvers can lead to innovation and discovery.
Challenges of Reverse Engineering
The task can often be very intricate, depending on the objective. Reverse engineering needs a thoroughly designed plan, the right set of labs and equipment, and the subject matter experts’ oversight to have a chance of success.
Additionally, there are regulations in most countries that may consider reverse engineering illegal and equivalent to stealing intellectual property. GHB Intellect takes intellectual property ownership very seriously and will not provide reverse engineering services when it is not legally permitted.
Benefits of Forward Engineering
Forward engineering brings new products to the market that offer unique designs and functions. Plus, there is little to no risk of an infringement on intellectual property as a new system is created.
Challenges of Forward Engineering
Forward engineering is of greater risk to a company. When decisions in product design are being made, it is difficult to pinpoint flaws in the system development. Problems can arise later when the product has been distributed, leading to callbacks and unsatisfied consumers. The time required to complete forward engineering is longer as the model must be precise and complete.
Conclusion
Forward engineering takes the given requirements and develops a new system that is wholly unique in design or function. The development requires a lot of time, and problems can arise if care is not taken in the system development stages.
Reverse engineering recovers data or architectural/procedural design information to build a representation of the application. It is useful to understand and examine the components and their relationships of an already established product and to detect product infringement. Through analysis, better products with increased effectiveness can enter the market, and the breakdown of parts can inspire innovation in the form of new products.
GHB Intellect Services
At GHB Intellect, reverse engineering is one of our core services to offer. With cadre of hundreds of subject matter experts, specialized labs and equipment, and decades of experience, we have the stand-out capability to reverse engineer all sorts of products, including circuitry, software/firmware code, processes, systems, networks, and protocols. Contact us today for more information.